 Ashraful's Blog
Ashraful's Blog Time to read: 4 min read
Introduction to Scylla DB

# What is Scylla DB?
Scylla is a realtime NoSQL database, written into C++ without changing the low level API of Apache Cassandra. So, it's an drop-in replacement for Apache Cassandra.
# Features
- NoSQL Database
- Open Source
- Good Performance
- Consistency
- Availability
- Scalability
- Drop-in replacement for Apache Cassandra
# Architecture
Scylla is a database that scales out and up. Scylla adopted much of its distributed scale-out design from the Apache Cassandra project (which adopted distribution concepts from Amazon Dynamo and data modeling concepts from Google BigTable).
# Node
A node is the basic unit of organization for a Scylla database. It is comprised of the Scylla database server software running on a computer server.
# Cluster
A Scylla cluster is consist of multiple nodes or Scylla instances. As we already know Scylla has built in flavor of distributed database system, So, Scylla visualized the nodes on a hash ring where multiple ring is connected to the hash.
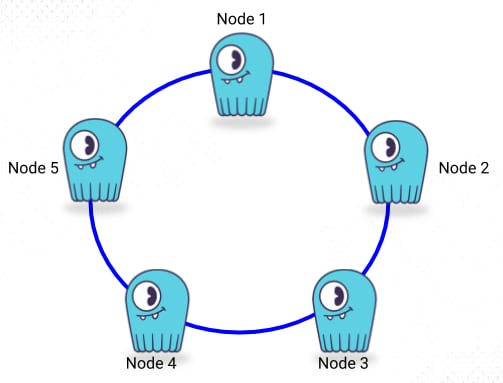
# Keyspace
A Scylla keyspace is a collection of tables with attributes that define how data is replicated on nodes. In general a keyspace is just like database in RDBMS.
# Performance
According to Scylla's documentation, Scylla has much better performance than Cassandra. A full post based on performance. Here, Scylla vs Cassandra Performance Benchmark (opens new window) 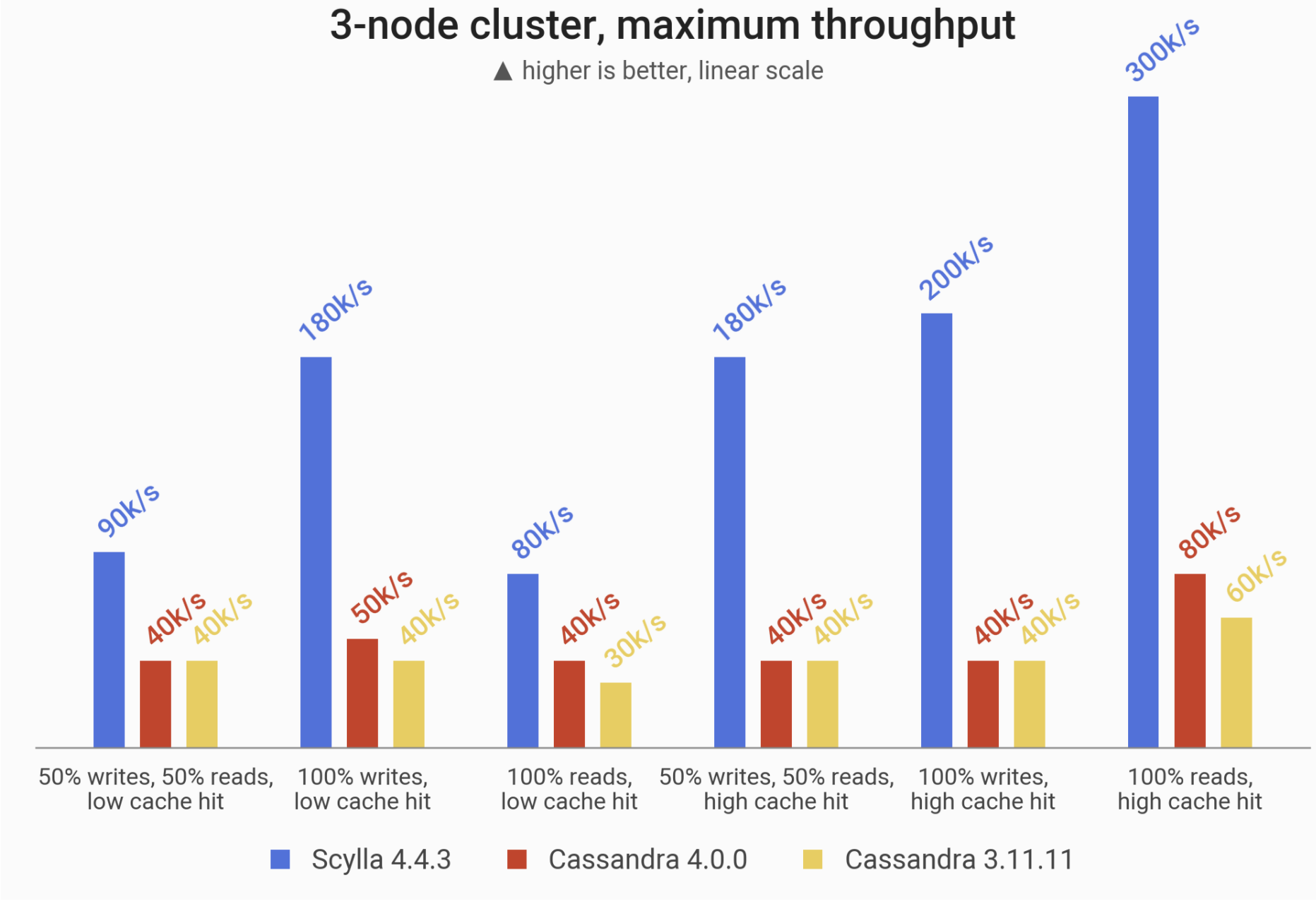
# Replication Factor
Scylla replicates data according to replication factor(RF). Basically number of RF is equal to the number of nodes in a cluster. But we can configure according to our need. For example, RF = 3 and number of nodes is 5. In this configuration scylla will write to two nodes per request out of three nodes.
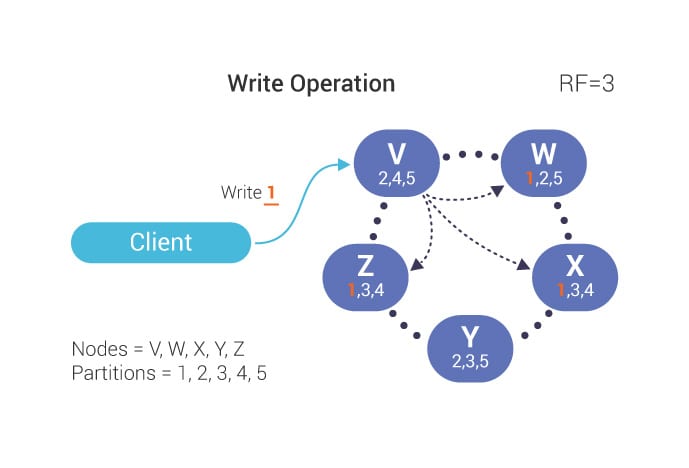
# Consistency Level
The Consistency Level (CL) determines how many replicas in a cluster must acknowledge a read or write operation before it is considered successful.
Some of the most common Consistency Levels used are:
- ANY – A write must be written to at least one replica in the cluster. A read waits for a response from at least one replica. It provides the highest availability with the lowest consistency.
- QUORUM – When a majority of the replicas respond, the request is honored. If RF=3, then 2 replicas respond. QUORUM can be calculated using the formula (n/2 +1) where n is the Replication Factor.
- ONE – If one replica responds; the request is honored.
- LOCAL_ONE – At least one replica in the local data center responds.
- LOCAL_QUORUM – A quorum of replicas in the local datacenter responds.
- EACH_QUORUM – (unsupported for reads) – A quorum of replicas in ALL datacenters must be written to.
- ALL – A write must be written to all replicas in the cluster, a read waits for a response from all replicas. Provides the lowest availability with the highest consistency.
# RF vs CL
Replication Factor(RF) and Consistency Level(CL) are too much related to performance and high availability. If CL is ALL then cluster is highly consistent but it might have unavailability. For example, if one node is down then the acknowledgement will not received so, it'll fail. Because we already configured to CL = ALL.
The following image has RF=3 and CL=1. It means during read/write servers will replicate to 3 nodes but only one acknowledgement is required to pass the request. So, it's highly available. If more than one nodes down data will not fail.
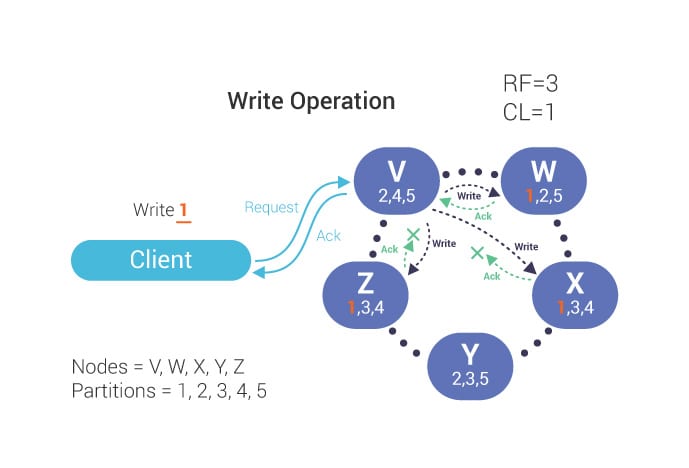
# Conclusion
To summarize, these are the main points we covered:
- Scylla has a ring-type architecture
- It’s a distributed, highly available, high performance, low maintenance, highly scalable NoSQL database
- In Scylla all nodes are created equal, there are no master/slave nodes
- Data is automatically distributed and replicated on the cluster according to the replication strategy
- Scylla supports multiple data centers